11 steps to be a great exporter
Md. Joynal Abdin, BBA (Hons.), MBA
Business Consultant & Digital Marketer
If you would you like to be an exporter? then, 11 steps to be a great exporter could be an useful article for you.
Exporters are instrumental in driving economic growth, creating employment opportunities, diversifying markets, earning foreign exchange, fostering innovation, and enhancing the competitiveness of businesses and industries. Their activities contribute to the development and prosperity of their home country while establishing strong economic ties with trading partners around the world.
Who is an exporter?
An exporter is a person or company that engages in international trade by selling goods or services to buyers located in other countries. Exporters play a crucial role in the global economy by promoting economic growth, creating jobs, and generating revenue for their respective countries.
Why you should be an exporter?
Exporting allows you to tap into new and larger markets beyond your domestic boundaries. By reaching international customers, you can significantly expand your customer base, increase sales potential, and diversify your revenue streams. This helps reduce dependence on a single market and provides opportunities for growth.
Entering international markets can often lead to higher profit margins. By targeting countries with higher purchasing power, lower production costs, or favorable exchange rates, you may be able to achieve better pricing and profitability compared to your domestic market.
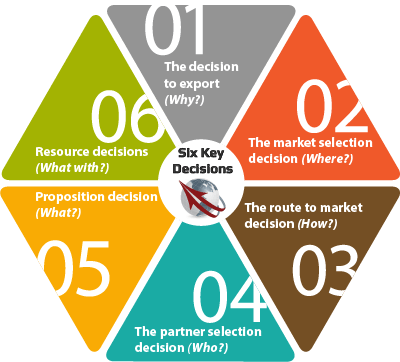
11 steps to be a great exporter:
- Exportability Assessment: Check your legal, organizational, logistical and managerial ability to become an exporter. It includes checking your prior ability and making necessary adjustment / taking necessary preparations to start exporting.
- Research and market analysis: Conduct thorough research to identify potential target markets for your products or services. Consider factors such as market size, demand, competition, cultural nuances, trade barriers, and regulatory requirements. Evaluate market entry strategies and assess the feasibility and profitability of exporting to different countries.
- Develop an export plan: Create a comprehensive export plan that outlines your objectives, target markets, marketing strategies, pricing, distribution channels, and logistics. This plan will serve as a road-map for your export activities and guide your decision-making process.
- Adapt your product or service: Analyze your offering to ensure it aligns with the preferences, regulations, and requirements of your target markets. Adapt your product packaging, labeling, or specifications, if necessary, to meet international standards and comply with local regulations.
- Establish legal and regulatory compliance: Familiarize yourself with export controls, trade regulations, and documentation requirements for each target market. Ensure compliance with international trade laws, export licenses, customs procedures, and any specific certifications or standards applicable to your product or service. For example you have to take export registration certificates (ERC) from CCI&E, Standard Certification from destination countries standard institution, and comply with other compulsory requirements etc.
- Pricing and payment: Develop a pricing strategy that considers factors such as production costs, transportation expenses, market demand, and competitive pricing in the target markets. Determine the most suitable payment methods, such as letters of credit, bank transfers, or online payment platforms, and ensure they align with your customers’ preferences and minimize financial risks.
- Logistics and distribution: Set up a reliable and efficient logistics infrastructure to handle the transportation, packaging, and delivery of your products. Identify suitable shipping methods, negotiate contracts with freight forwarders or shipping lines, and ensure compliance with export documentation requirements, including invoices, packing lists, and shipping instructions.
- Establish sales and marketing channels: Develop a marketing plan tailored to each target market. Identify potential sales agents, distributors, or representatives who have local market knowledge and established networks. Leverage digital marketing tools, attend trade shows or exhibitions, and establish an online presence to promote your products or services to international customers.
- Risk management and insurance: Assess and mitigate potential risks associated with exporting, such as non-payment, political instability, or logistical challenges. Consider obtaining export credit insurance, trade finance solutions, or other risk management tools to protect your business against unforeseen events.
- Build relationships and networks: Cultivate relationships with potential customers, local partners, industry associations, and government agencies in your target markets. Attend trade missions, business forums, and networking events to establish connections and gain market insights. Building strong relationships can enhance your market penetration and provide valuable support for your export activities.
- Continuous mentorship, evaluation and adaptation: Regularly review and evaluate your export performance. Monitor market trends, customer feedback, and competitors’ activities to adapt your strategies and offerings accordingly. Continuously seek opportunities for improvement, innovation, and expansion into new markets.
Benefits of export for the country:
Exporting offers numerous benefits for businesses, contributing to their growth, profitability, and overall success. Here are some key benefits of exporting:
- Increased sales and revenue: Exporting opens up new markets and customer bases, allowing businesses to increase their sales potential significantly. By targeting international markets, businesses can tap into larger consumer populations and benefit from increased demand, leading to higher revenue streams.
- Diversification and risk mitigation: Expanding into international markets helps businesses diversify their customer base and reduce dependence on a single market. This diversification provides a buffer against economic downturns or fluctuations in specific markets, spreading business risk across different countries and regions.
- Profitability and improved margins: Exporting can often lead to higher profit margins for businesses. By accessing markets with higher purchasing power, lower production costs, or favorable exchange rates, businesses may achieve better pricing and profitability compared to their domestic market.
- Economies of scale and increased production efficiency: Entering new markets can drive economies of scale, enabling businesses to increase production levels and optimize their operations. With larger production volumes, businesses can benefit from improved efficiencies, reduced costs per unit, and increased competitiveness.
- Access to new opportunities and untapped markets: Exporting provides access to new opportunities and untapped markets that may not be available domestically. Businesses can identify niche markets or segments with specific needs and preferences that align well with their products or services, allowing them to gain a competitive advantage.
- Innovation and product improvement: Engaging in international trade exposes businesses to diverse market demands and competition. This exposure encourages businesses to innovate, improve product quality, and develop new features or variations to meet the requirements of different markets. This drive for innovation can benefit both exported and domestic products.
- Brand recognition and reputation: Successful exporting can enhance a business’s brand recognition and reputation. Establishing a presence in international markets showcases a business’s ability to compete globally, indicating quality, reliability, and credibility. A strong export reputation can positively impact a business’s domestic market performance as well.
- Learning and knowledge transfer: Exporting involves engaging with different cultures, business practices, and market trends. This exposure allows businesses to gain valuable insights, expand their knowledge, and adopt best practices from international partners. These learnings can be applied to enhance business operations and competitiveness.
- Access to resources and partnerships: Exporting often leads to the establishment of valuable partnerships and access to resources that may not be readily available domestically. Businesses can collaborate with international suppliers, distributors, or research institutions, benefiting from shared knowledge, expertise, and resources that can contribute to their growth and competitiveness.
- Overall business growth and sustainability: Exporting can fuel long-term business growth and sustainability. By capitalizing on global market opportunities, businesses can expand their operations, create new jobs, and contribute to the economic development of their home country. Sustainable export growth strengthens the business’s position in the market and enhances its ability to withstand economic fluctuations.
Advantages of Export:
- Increased sales and revenue: Exporting allows businesses to access larger markets and tap into new customer bases, leading to increased sales potential and revenue streams.
- Diversification and risk mitigation: Expanding into international markets helps businesses diversify their customer base, reducing dependence on a single market and mitigating risks associated with economic fluctuations or changes in specific markets.
- Economies of scale: Exporting can lead to increased production volumes, allowing businesses to benefit from economies of scale, improved efficiencies, and reduced costs per unit.
- Enhanced profitability: By targeting markets with higher purchasing power or favorable exchange rates, businesses can often achieve better pricing and profit margins, leading to increased profitability.
- Access to new opportunities and untapped markets: Exporting opens up new opportunities to reach untapped markets that may not be available domestically, allowing businesses to expand their customer base and gain a competitive advantage.
Disadvantages of Export:
- Market entry barriers: Entering new markets can present various barriers such as trade regulations, customs procedures, legal requirements, and cultural differences, which may require additional time, resources, and expertise to navigate.
- Increased complexity and operational challenges: Exporting involves dealing with international logistics, shipping, customs clearance, and documentation requirements, which can be complex and require additional administrative efforts and costs.
- Currency exchange risks: Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the profitability of export transactions. Currency volatility may result in price fluctuations, affecting the competitiveness and profitability of exported products.
Finally; we can state that, exporters are instrumental in driving economic development by creating employment opportunities, generating foreign exchange earnings, diversifying the economy, fostering innovation, enhancing productivity, attracting foreign investment, and contributing to infrastructure development. Their activities stimulate economic growth, improve living standards. To make your company exportable you can contact us.





0 Comments